Accessory Navicular
What is Accessory Navicular?
Os Navicularum
What is the Accessory Navicular?
The accessory navicular (os navicularum or os tibiale externum) is an extra bone or piece of cartilage located on the inner side of the foot just above the arch. It is incorporated within the posterior tibial tendon, which attaches in this area.
An accessory navicular is present from birth and is not part of normal bone structure.
What is Accessory Navicular Syndrome?
People who have an accessory navicular often are unaware of the condition if it causes no problems. However, some people with this extra bone develop a painful condition known as accessory navicular syndrome when the bone or posterior tibial tendon are aggravated. This can result from any of the following:
- Trauma, as in a foot or ankle sprain.
- Chronic irritation from shoes.
- Excessive activity or overuse.
Many people with accessory navicular syndrome also have flat feet. Having a flat foot puts more strain on the posterior tibial tendon, which can produce inflammation or irritation of the accessory navicular.
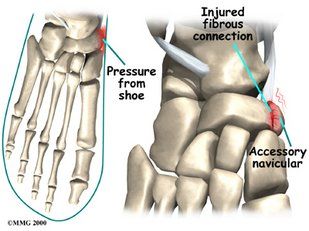
Causes
Symptoms
Adolescence is a common time for the symptoms to first appear. The signs and symptoms of accessory navicular syndrome include:
- A visible bony prominence on the midfoot (the inner side of the foot, just above the arch).
- Redness and swelling.
- Vague pain or throbbing in the midfoot and arch.
Diagnosis
To diagnose accessory navicular syndrome, the foot and ankle surgeon will ask about symptoms and examine the foot, looking for skin irritation or swelling. The doctor may press on the bony prominence to assess the area for discomfort. Foot structure, muscle strength, joint motion, and the way the patient walks may also be evaluated.
If accessory navicular syndrome looks likely, X-rays are usually ordered to confirm the diagnosis. If there is ongoing pain or inflammation, an MRI or other advanced imaging tests may be used to further evaluate the condition.
Non-surgical Treatment
The goal of non-surgical treatment for accessory navicular syndrome is to relieve the symptoms. The following may be used:
- Immobilization.
- Ice.
- Medications. In some cases, oral or injected steroid medications may be used in combination with immobilization to reduce pain and inflammation.
- Physical therapy.
- Orthotic devices.
Even after successful treatment, the symptoms of accessory navicular syndrome sometimes reappear. When this happens, non-surgical approaches are usually repeated.
When is Surgery Needed?
To diagnose accessory navicular syndrome, the foot and ankle surgeon will ask about symptoms and examine the foot, looking for skin irritation or swelling. The doctor may press on the bony prominence to assess the area for discomfort. Foot structure, muscle strength, joint motion, and the way the patient walks may also be evaluated.
If accessory navicular syndrome looks likely, X-rays are usually ordered to confirm the diagnosis. If there is ongoing pain or inflammation, an MRI or other advanced imaging tests may be used to further evaluate the condition.


