Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction
What is Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction?
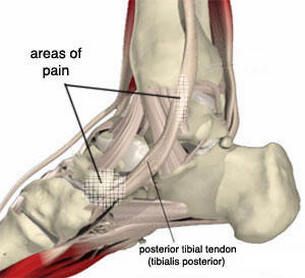
The posterior tibial tendon serves as one of the major supporting structures of the foot, helping it to function while walking. Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction (PTTD) is a condition caused by changes in the tendon, impairing its ability to support the arch. This results in flattening of the foot.
PTTD the most common type of flatfoot developed during adulthood. Although it typically occurs in only one foot, some people may develop it in both feet.
Causes
Overuse of the posterior tibial tendon is often the cause of PTTD. Symptoms usually occur after activities that involve the tendon, such as running, walking, hiking, or climbing stairs.
Symptoms
The symptoms of PTTD may include pain, swelling, a flattening of the arch, and an inward rolling of the ankle. As the condition progresses, the symptoms will change.
When PTTD initially develops, there is pain on the inside of the foot and ankle (along the tendon). In addition, the area may become swollen.
Later, as the arch begins to flatten, there may still be pain on the inside of the foot and ankle and the foot and toes begin to turn outward while the ankle rolls inward.
As PTTD becomes more advanced, the arch flattens even more and the pain often shifts to the outside of the foot, below the ankle. The tendon has deteriorated considerably, and arthritis often develops in the foot. In more severe cases, arthritis may also develop in the ankle.
Diagnosis
Non-surgical Treatment
Because of the progressive nature of PTTD, early treatment is advised. If treated early enough, your symptoms may resolve without the need for surgery and progression of your condition can be arrested.
In contrast, untreated PTTD could leave you with an extremely flat foot and pain in the foot and ankle, and increasing limitations on walking, running, or other activities.
In many cases of PTTD, treatment can begin with non-surgical approaches that may include:
- Orthotic devices or bracing.
- Immobilization.
- Physical therapy.
- Medications.
- Shoe modifications.
When is Surgery Needed?
Complete and comprehensive spectrum of both diagnosis and treatments
QUICK LINKS
ABOUT
Specialist Foot and Ankle Surgery and Consultation in Manchester. Our specialist team of surgeons and podiatrists provide the highest level of expertise in the effective management of any foot and ankle condition. .
Manchester Foot And Ankle Clinic / North West OrthoSports is a Registered Trade Mark
North West OrthoSports / Manchester Foot & Ankle Clinic Ltd
93-107 . Lancefield Steet
Glasgow .G3 8HZ
Limited Company-387376
VAT Registration - 214 0705 54
Please See Our Legal Disclaimer on Online Medical Advice
All Rights Reserved | Manchester Foot And Ankle Clinic | Privacy Policy


